Java Code To Generate Public And Private Keys
- Java Code To Generate Public And Private Keys 2017
- Java Code To Generate Public And Private Keys Are The Same In A Public Key Encryption Scheme
May 07, 2019 Storing asymmetric keys is a bit more complex since we need to deal with certificate chains. Also, the KeyStore API gives us a dedicated method called setKeyEntry which is more convenient than the generic setEntry method. So, to save an asymmetric key, we'll need four things: an alias, same as before; a private key. Because we aren't using the. Recall from the Generate Public and Private Keys step that the public key was placed in a PublicKey object named pub.You can get the encoded key bytes by calling the getEncoded method and then store the encoded bytes in a file. You can name the file whatever you want. If, for example, your name is Susan, you might name it something like suepk (for 'Sue's public key'), as in the following. You can generate Certificate in java dynamically, by using a pair or keys. (Public Key, Private Keys). Get These keys as BigInteger format and checking the following code to generate certificate.
| importjava.security.KeyPairGenerator; |
| importjava.security.KeyPair; |
| importjava.security.PrivateKey; |
| importjava.security.PublicKey; |
| importjava.security.KeyFactory; |
| importjava.security.spec.EncodedKeySpec; |
| importjava.security.spec.PKCS8EncodedKeySpec; |
| importjava.security.spec.X509EncodedKeySpec; |
| importjava.security.spec.InvalidKeySpecException; |
| importjava.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException; |
| importcom.sun.jersey.core.util.Base64; |
| publicclassGeneratePublicPrivateKeys { |
| privatestaticvoidgenerateKeys(StringkeyAlgorithm, intnumBits) { |
| try { |
| // Get the public/private key pair |
| KeyPairGenerator keyGen =KeyPairGenerator.getInstance(keyAlgorithm); |
| keyGen.initialize(numBits); |
| KeyPair keyPair = keyGen.genKeyPair(); |
| PrivateKey privateKey = keyPair.getPrivate(); |
| PublicKey publicKey = keyPair.getPublic(); |
| System.out.println('n'+'Generating key/value pair using '+ privateKey.getAlgorithm() +' algorithm'); |
| // Get the bytes of the public and private keys |
| byte[] privateKeyBytes = privateKey.getEncoded(); |
| byte[] publicKeyBytes = publicKey.getEncoded(); |
| // Get the formats of the encoded bytes |
| String formatPrivate = privateKey.getFormat(); // PKCS#8 |
| String formatPublic = publicKey.getFormat(); // X.509 |
| System.out.println('Private Key : '+Base64.encode(String.valueOf(privateKeyBytes))); |
| System.out.println('Public Key : '+Base64.encode(String.valueOf(publicKeyBytes))); |
| // The bytes can be converted back to public and private key objects |
| KeyFactory keyFactory =KeyFactory.getInstance(keyAlgorithm); |
| EncodedKeySpec privateKeySpec =newPKCS8EncodedKeySpec(privateKeyBytes); |
| PrivateKey privateKey2 = keyFactory.generatePrivate(privateKeySpec); |
| EncodedKeySpec publicKeySpec =newX509EncodedKeySpec(publicKeyBytes); |
| PublicKey publicKey2 = keyFactory.generatePublic(publicKeySpec); |
| // The original and new keys are the same |
| System.out.println(' Are both private keys equal? '+ privateKey.equals(privateKey2)); |
| System.out.println(' Are both public keys equal? '+ publicKey.equals(publicKey2)); |
| } catch (InvalidKeySpecException specException) { |
| System.out.println('Exception'); |
| System.out.println('Invalid Key Spec Exception'); |
| } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) { |
| System.out.println('Exception'); |
| System.out.println('No such algorithm: '+ keyAlgorithm); |
| } |
| } |
| publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args) { |
| // Generate a 1024-bit Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA) key pair |
| generateKeys('DSA', 1024); |
| // Generate a 576-bit DH key pair |
| generateKeys('DH', 576); |
| // Generate a 1024-bit RSA key pair |
| generateKeys('RSA', 1024); |
| } |
| } |
commented Mar 14, 2018
Java Code To Generate Public And Private Keys 2017
Hi You post is interestnig , is there away I can create a privatre key instance via a signature given stiring? I have pub/private keys generated already KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator is going to createa key pair, but in my case I alrady have it and then further want to use them for signign. e.g //ecdsaSign.initSign(keyPair.getPrivate()); |
Contents
- 3. Saving the Keys in Binary Format
- Source Code
1. Introduction
Let us learn the basics of generating and using RSA keys in Java.
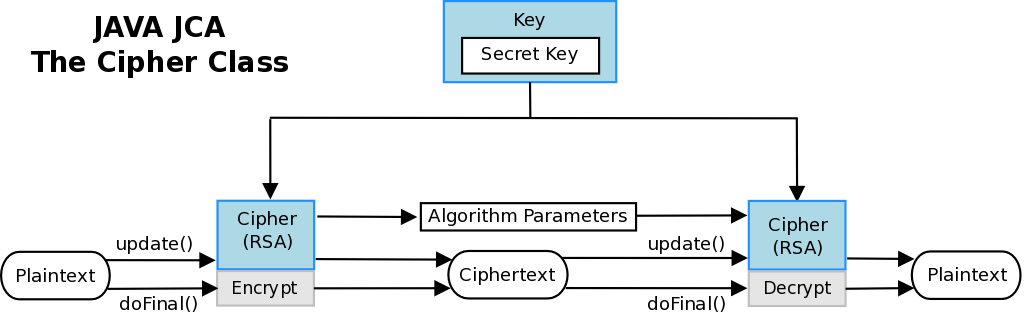
Java provides classes for the generation of RSA public and private key pairs with the package java.security. You can use RSA keys pairs in public key cryptography.
Public key cryptography uses a pair of keys for encryption. Distribute the public key to whoever needs it but safely secure the private key.
Public key cryptography can be used in two modes:
Encryption: Only the private key can decrypt the data encrypted with the public key.
Authentication: Data encrypted with the private key can only be decrypted with the public key thus proving who the data came from.
2. Generating a Key Pair
First step in creating an RSA Key Pair is to create a KeyPairGeneratorfrom a factory method by specifying the algorithm (“RSA” in this instance):
Initialize the KeyPairGenerator with the key size. Use a key size of 1024 or 2048. Currently recommended key size for SSL certificates used in e-commerce is 2048 so that is what we use here.
From the KeyPair object, get the public key using getPublic() and the private key using getPrivate().
3. Saving the Keys in Binary Format
Save the keys to hard disk once they are obtained. This allows re-using the keys for encryption, decryption and authentication.
What is the format of the saved files? The key information is encoded in different formats for different types of keys. Here is how you can find what format the key was saved in. On my machine, the private key was saved in PKCS#8 format and the public key in X.509 format. We need this information below to load the keys.
3.1. Load Private Key from File
After saving the private key to a file (or a database), you might need to load it at a later time. You can do that using the following code. Note that you need to know what format the data was saved in: PKCS#8 in our case.
3.2 Load Public Key from File
Load the public key from a file as follows. The public key has been saved in X.509 format so we use the X509EncodedKeySpec class to convert it.
4. Use Base64 for Saving Keys as Text
Save the keys in text format by encoding the data in Base64. Java 8 provides a Base64 class which can be used for the purpose. Save the private key with a comment as follows:
And the public key too (with a comment):
5. Generating a Digital Signature
Java Code To Generate Public And Private Keys Are The Same In A Public Key Encryption Scheme
As mentioned above, one of the purposes of public key cryptography is digital signature i.e. you generate a digital signature from a file contents, sign it with your private key and send the signature along with the file. The recipient can then use your public key to verify that the signature matches the file contents.
Here is how you can do it. Use the signature algorithm “SHA256withRSA” which is guaranteed to be supported on all JVMs. Use the private key (either generated or load from file as shown above) to initialize the Signatureobject for signing. It is then updated with contents from the data file and the signature is generated and written to the output file. This output file contains the digital signature and must be sent to the recipient for verification.
6. Verifying the Digital Signature
The recipient uses the digital signature sent with a data file to verify that the data file has not been tampered with. It requires access to the sender’s public key and can be loaded from a file if necessary as presented above.
The code below updates the Signature object with data from the data file. It then loads the signature from file and uses Signature.verify() to check if the signature is valid.
And that in a nutshell is how you can use RSA public and private keys for digital signature and verification.
Source Code
Go here for the source code.
